RFID USB (AADD)
RFID (radio frequency identification) systems use data strings stored inside RFID tags or transponders) to uniquely identify people or objects when they are scanned by an RFID reader. These types of systems are found in many applications such as passport protection, animal identification, inventory control systems, and secure access control systems, robotics, navigation, inventory tracking, payment systems, and car immobilization.
10
People watching this product now!
Description
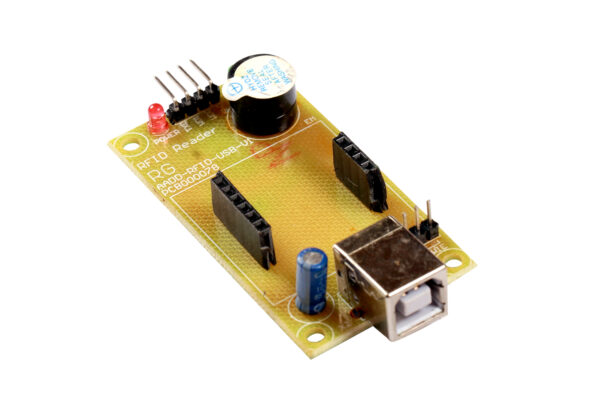
RFID USB (AADD)
The RFID RDM6300 Reader Author reads EM4100 household transponder tags which are introduced in proximity to the reader and output the distinctive tag quantity by RS232 interface @9600 bps. The reader output 12 byte together with one begin, cease byte and 10 distinctive knowledge byte. The beginning byte and cease byte are used to simply determine {that a} right string has been acquired from the reader (they correspond to a printing operation and printing operation characters, respectively). The center ten bytes are the precise tag’s distinctive ID. Vertical and horizontal parity checking has been worn out card studying algorithm to verify knowledge integrity.
One standing LED is supplied to level card detection. The conventional detection vary is 10-15CM for Card Sort TAGs. The RFID Reader (as effectively as a result of the RFID tags makes use of the EM4102 protocol. Some other tags that additionally use the EM4102 protocol can be utilized with the RFID reader. All communication is 8 knowledge bits, no parity, 1 cease bit, non-inverted, least vital bit first (8N1). The baud is configured for 9600bps, a typical communications pace supported by most any microprocessor or PC, and cannot be modified. The RFID Reader Module initiates all communication. The RFID Reader Module can join on to an RS232-compatible interface (PC) or to any suitable UART by utilizing an exterior degree shifter. RFID (radio frequency identification) techniques use knowledge strings saved inside RFID tags or transponders) to uniquely determine individuals or objects as soon as they’re scanned by an RFID reader.
Most of these techniques are discovered in lots of functions corresponding to passport safety, animal identification, stock management techniques, and safe entry management techniques, robotics, navigation, stock monitoring, fee techniques, and automotive immobilization. As a result of passive tags require a sturdy RF area to work, their efficient vary is restricted to a neighbourhood in shut proximity to the RFID reader. The space over which the RFID tag is usable is affected by such issues as a result of the tag form and measurement, supplies getting used inside the space close to the reader, and the orientation of the reader and tag in reference to 1 one other and of their working atmosphere. The smaller a tag, the nearer it should be to the reader to work. Every transponder tag comprises a singular identifier (considered one of 1,099,511,627,776, attainable mixtures) that’s learn by the RFID Reader Module and transmitted to the host through a easy serial interface.
There are a variety of transponder tags which are accessible completely different packages. Every tag has a particular vary that’s inside 10% of the given distance for every kind of tag. The explanation for the ten is because of environmental situations and RFID modules.